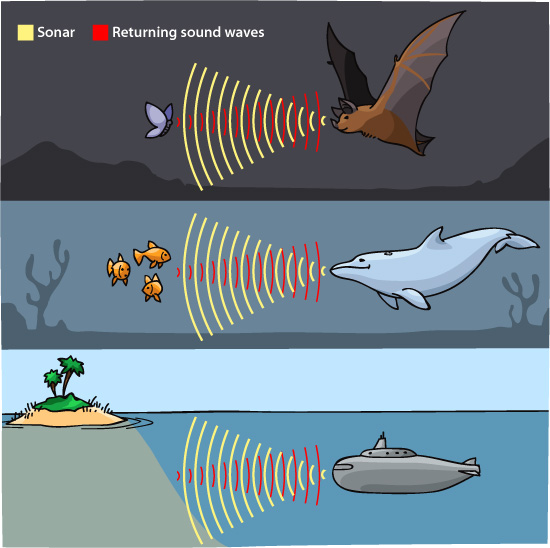
Bats Echolocation Predators . bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues.
from sciencebehindsuperpowers.weebly.com
these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same?
Echolocation
Bats Echolocation Predators if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same?
From www.pnas.org
Modeling active sensing reveals echo detection even in large groups of Bats Echolocation Predators They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.cell.com
Neural coding of 3D spatial location, orientation, and action selection Bats Echolocation Predators insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? bats have been reported to have echo detection. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT pt 2 sensory input ch 2 echolocation in bats bat behavior Bats Echolocation Predators these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound.. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Probing the Natural Scene by Echolocation in Bats Bats Echolocation Predators bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. insectivorous bats that. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From chxout.com
Bats and echolocation how does it work? chXout Bats Echolocation Predators these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.earth.com
How bats use echolocation to hunt prey • Bats Echolocation Predators these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.youtube.com
Echolocation in bats YouTube Bats Echolocation Predators if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
The challenge of detecting prey Private and social information use in Bats Echolocation Predators if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25). Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.batconservationireland.org
Echolocation Bat Conservation Ireland Bats Echolocation Predators if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.getbatsout.com
Are Bats Blind? Bats Echolocation Predators these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.alamy.com
Echolocation (biosonar) in bats Stock Photo Alamy Bats Echolocation Predators They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.dreamstime.com
Echolocation in Bats and Dolphins,Dolphins and Bats Hunt Their Prey by Bats Echolocation Predators insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound.. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From dxolkatfw.blob.core.windows.net
Bat Echolocation Journals at Tena Hewett blog Bats Echolocation Predators insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? bats have been reported to have echo detection. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.researchgate.net
Bat echolocation methodology for prey discovery Download High Bats Echolocation Predators insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound.. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.youtube.com
Bat Echolocation YouTube Bats Echolocation Predators bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. insectivorous bats that capture prey in the air need to continuously determine the position of prey while. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From stock.adobe.com
Bat echolocation. Bio sonar. Butterfly, insect, fly navigate. Reflected Bats Echolocation Predators these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. insectivorous bats that capture prey. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From www.researchgate.net
Comparative sizes of predator, prey and echolocation signal for the big Bats Echolocation Predators bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey, but the bats also use echolocation cues. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. if owls, and. Bats Echolocation Predators.
From austinbatrefuge.org
Echolocation Bat Detectors Austin Bat Refuge Bats Echolocation Predators bats have been reported to have echo detection thresholds from 0 (24) to 55 db re 20 pa (25) in laboratory experiments. if owls, and other nocturnal predators, evolved large eyes to see and hunt at night, why didn’t bats do the same? these predatory bats primarily use sound of the frog's call to find their prey,. Bats Echolocation Predators.